Quickstart¶
ML Tooling requires you to create a data class inheriting from one of the ML Tooling dataclasses Dataset, FileDataset, SQLDataset.
You have to define two methods in your class:
Defines how to your training data is loaded - whether it’s reading from an excel file or loading from a database. This method should read in your data and return a DataFrame containing your features and a target - usually as a numpy array or a pandas Series. This method is called the first time ML Tooling needs to gather data and is only called once.
Defines how to load your prediction data. When predicting, you have to tell ML Tooling what data to load in. Usually this takes an argument to select features for a given customer or item.
>>> from ml_tooling import Model
>>> from ml_tooling.data import Dataset
>>> from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
>>> import pandas as pd
>>>
>>> class BostonData(Dataset):
... def load_training_data(self):
... data = load_boston()
... return pd.DataFrame(data.data, columns=data.feature_names), data.target
...
... # Define where to get prediction time data - returning a DataFrame
... def load_prediction_data(self, idx):
... data = load_boston()
... x = pd.DataFrame(data.data, labels=data.feature_names)
... return x.loc[idx] # Return given observation
>>>
>>> # Use your data with a given model
>>> data = BostonData()
To create a model, use the Model class by giving it an estimator to instantiate the class. The estimator must use scikit-learn’s standard API.
>>> regression = Model(LinearRegression())
>>> regression
<Model: LinearRegression>
Now we can train our model. We start by splitting the data into training and test data
by calling create_train_test()
>>> data.create_train_test()
<BostonData - Dataset>
>>> result = regression.score_estimator(data)
>>> result
<Result LinearRegression: {'r2': 0.68}>
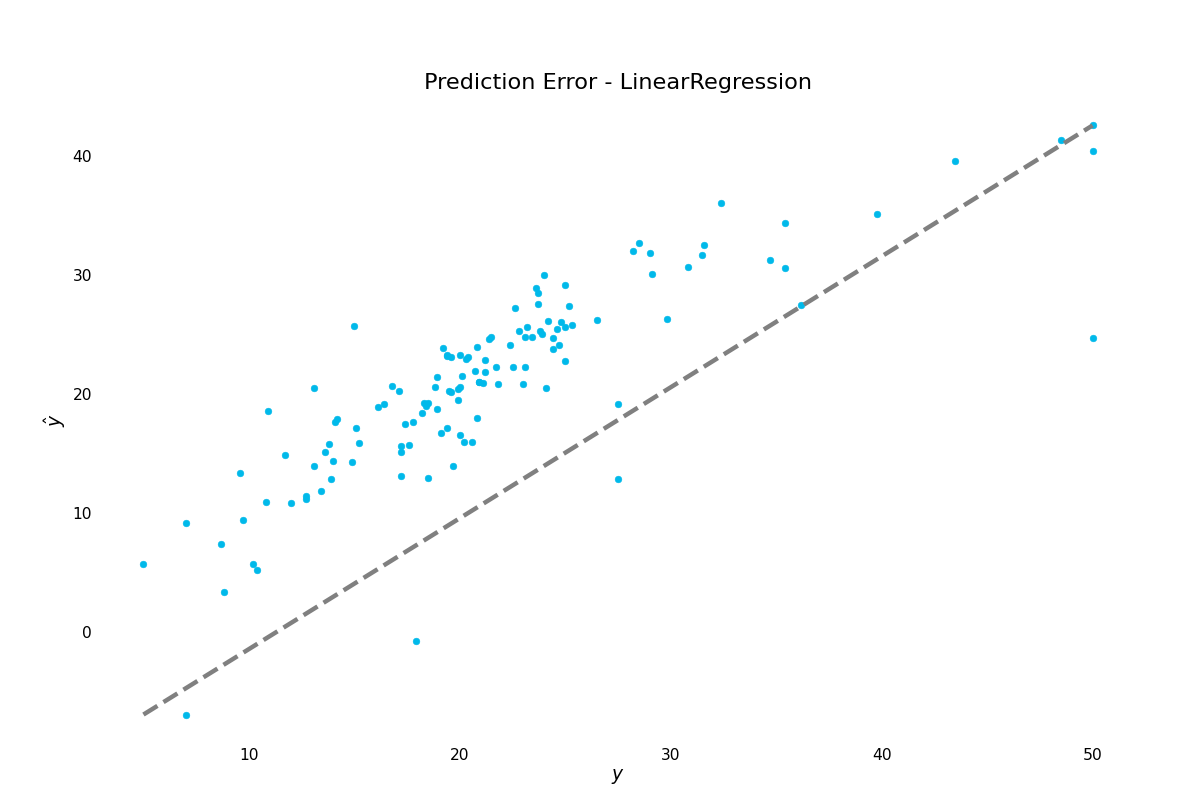
We can plot the prediction errors:
>>> result.plot.prediction_error()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
We can save and load our model:
>>> from ml_tooling.storage import FileStorage
>>> storage = FileStorage('./estimator_dir')
>>> file_path = regression.save_estimator(storage)
>>> my_new_model = regression.load_estimator(file_path.name, storage=storage)
>>> my_new_model
<Model: LinearRegression>
We can try out many different models:
>>> from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge, LassoLars
>>> models_to_try = [LinearRegression(), Ridge(), LassoLars()]
>>> best_model, all_results = Model.test_estimators(data,
... models_to_try,
... metrics='neg_mean_squared_error')
>>> all_results
ResultGroup(results=[<Result LinearRegression: {'neg_mean_squared_error': -22.1}>, <Result Ridge: {'neg_mean_squared_error': -22.48}>, <Result LassoLars: {'neg_mean_squared_error': -72.26}>])
We get the results in sorted order for each model and see that LinearRegression gives us the best result!
Continue to Tutorial